Preeclampsia can be a life-threatening condition for both mother and baby if not treated properly. In this article, we’ll take an in-depth look at preeclampsia – what it is, the risk factors associated with it, and the treatments available to ensure the safety of both mother and baby. With all this information, you can make sure that you are well informed about this serious condition.
Introduction to Preeclampsia
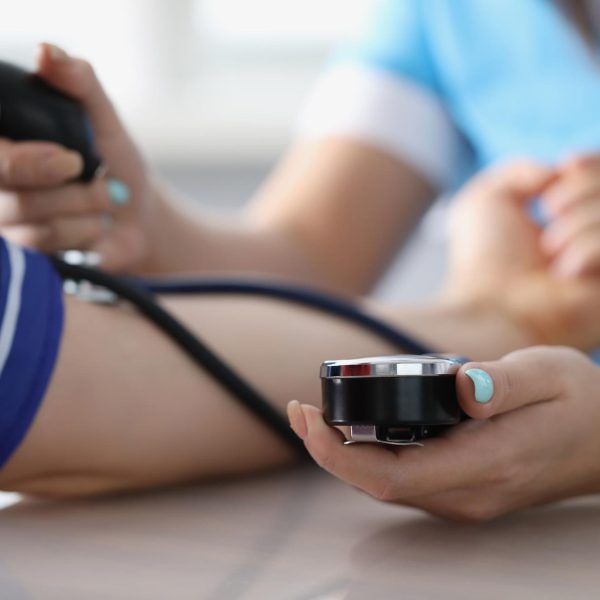
preeclampsia is a disorder that can occur during pregnancy, typically after the 20th week. It is characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine. Preeclampsia can lead to serious or even life-threatening complications for both the mother and baby.
There are two types of preeclampsia: early-onset and late-onset. Early-onset preeclampsia occurs before 34 weeks of pregnancy. Late-onset preeclampsia occurs after 34 weeks of pregnancy.
Risk factors for Preeclampsia
• Age: Women who are younger than 20 years old or older than 40 years old are at increased risk.
• Obesity: Women who are obese (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2) are at increased risk.
• Family history: Women with a family history of preeclampsia are at increased risk.
• Previous history: Women who have had preeclampsia in a previous pregnancy are at increased risk.
• Multiple gestations: Women who are pregnant with more than one baby are at increased risk.
Causes of Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is a pregnancy complication that can occur after the 20th week of gestation. It is marked by high blood pressure and protein in the urine. While the exact cause of preeclampsia is unknown, it is thought to be related to problems with the placenta.
Symptoms of Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is a condition that can occur during pregnancy. The symptoms of preeclampsia include high blood pressure, swelling in the hands and feet, protein in the urine, and headaches. Preeclampsia can be a dangerous condition for both the mother and the baby. If you are pregnant and have any of these symptoms, you should contact your healthcare provider.
Diagnosing Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is a serious pregnancy complication that can occur after the 20th week of gestation. It is characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine. Preeclampsia can lead to organ damage and even death if left untreated.
There are several ways to diagnose preeclampsia. The most common method is through a physical examination. Your doctor will check your blood pressure and look for signs of protein in your urine. Other tests that may be used to diagnose preeclampsia include:
-Blood tests to check for levels of certain proteins or enzymes
-Urinalysis to check for protein or red blood cells in the urine
-Ultrasound to assess the size and health of the placenta
If you are diagnosed with preeclampsia, it is important to receive treatment as soon as possible. Treatment typically involves close monitoring of your blood pressure and daily urine tests. You may also be placed on bed rest and/or given medication to help lower your blood pressure. In some cases, early delivery of the baby may be necessary.

Treatments for Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is a serious pregnancy complication that can lead to organ damage and even death. It typically occurs after the 20th week of pregnancy and is characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine. While there is no cure for preeclampsia, treatments are available to help manage the condition and minimize its complications.
Medical treatment for preeclampsia typically involves close monitoring of blood pressure and urine output. If the condition worsens, hospitalization may be necessary so that mothers can be monitored more closely. Bed rest, magnesium sulfate, and blood transfusions may also be recommended in severe cases. Delivery of the baby is often the best way to treat preeclampsia, even if it means delivering early.
If you are diagnosed with preeclampsia, it is important to follow your doctor’s orders and take all recommended precautions. With proper treatment, most women with preeclampsia will go on to have healthy pregnancies and babies.
Prevention of Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is a serious medical condition that can occur during pregnancy. It is characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine. Preeclampsia can lead to serious complications, including seizures, organ damage, and even death. The best way to prevent preeclampsia is to get regular prenatal care. This includes regular checkups, blood pressure checks, and urine tests. If you have any risk factors for preeclampsia, your doctor may recommend additional tests or treatments.
Read more: Prenatal Care for Each Trimester
Conclusion
Preeclampsia is a serious medical condition that can affect pregnant women and should not be taken lightly. If you are experiencing any of the signs or symptoms associated with preeclampsia, it’s essential to contact your doctor immediately for diagnosis and treatment. It’s also important to understand the risk factors associated with preeclampsia so that you can take steps to reduce your chances of developing this condition during pregnancy. By arming yourself with knowledge about preeclampsia, you’ll be better prepared if faced with this potentially dangerous situation in the future.
Read more: Healthy Habits to Form During Pregnancy


























Share this article